Creating a green yard is not only beneficial for the environment but also enhances the beauty and productivity of your outdoor space. With the increasing focus on eco-friendly gardening techniques, more gardeners are turning to sustainable practices that minimize environmental impact while promoting biodiversity and soil health. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, adopting these methods can help you grow vibrant plants, reduce waste, and support local ecosystems. From organic soil management to natural pest control, there are countless ways to make your garden more eco-conscious. This article explores eco-friendly gardening techniques that are easy to implement and offer long-term benefits for both your garden and the planet.
Table of Contents
ToggleOrganic Soil Management: The Foundation of Eco-Friendly Gardening Techniques
Healthy soil is the cornerstone of any thriving garden, and eco-friendly gardening techniques often begin with organic soil management. Traditional gardening methods frequently rely on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can leach into groundwater and harm beneficial microorganisms. By contrast, organic practices prioritize natural amendments that enrich the soil without introducing harmful chemicals.
One of the most effective eco-friendly gardening techniques is the use of compost. Composting transforms kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials into nutrient-rich soil enhancers. To start, collect materials like fruit peels, coffee grounds, and fallen leaves, then pile them in a bin or designated area. As the compost breaks down, it releases essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which nourish plants without the need for artificial fertilizers. This process also reduces landfill waste, as organic matter that would otherwise decompose in a trash bin is repurposed to benefit your garden.
Another key practice is mulching, which helps retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate temperature. Organic mulches like straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves gradually decompose, adding organic matter to the soil and improving its structure over time. This not only reduces the need for frequent watering—saving energy and resources—but also minimizes the use of synthetic herbicides. For example, mulch can prevent weed growth, which in turn reduces the amount of chemical sprays required to maintain a clean garden bed.
To further enhance soil quality, eco-friendly gardening techniques recommend avoiding chemical pesticides and opting for natural alternatives. For instance, planting cover crops such as clover or rye during off-seasons can prevent soil erosion and add nitrogen to the soil through nitrogen-fixing properties. Additionally, crop rotation helps maintain soil fertility by preventing nutrient depletion in specific areas. By rotating plants like legumes, vegetables, and flowers, you ensure that each section of the garden receives a balanced mix of nutrients.
Water Conservation: Eco-Friendly Gardening Techniques for Efficient Water Use
Water is a precious resource, and eco-friendly gardening techniques emphasize conserving it to reduce waste and lower utility bills. A significant portion of household water usage goes toward maintaining lawns and gardens, making efficient water management crucial for sustainability.
One of the simplest eco-friendly gardening techniques is drip irrigation. Unlike traditional sprinkler systems, which can lose up to 50% of water to evaporation and runoff, drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots of plants through a network of tubes and emitters. This method ensures that every drop is used effectively, promoting healthy plant growth while minimizing water consumption. To install a drip system, you can use soil-based or plastic tubing, connect it to a faucet or water source, and place emitters near each plant’s root zone.
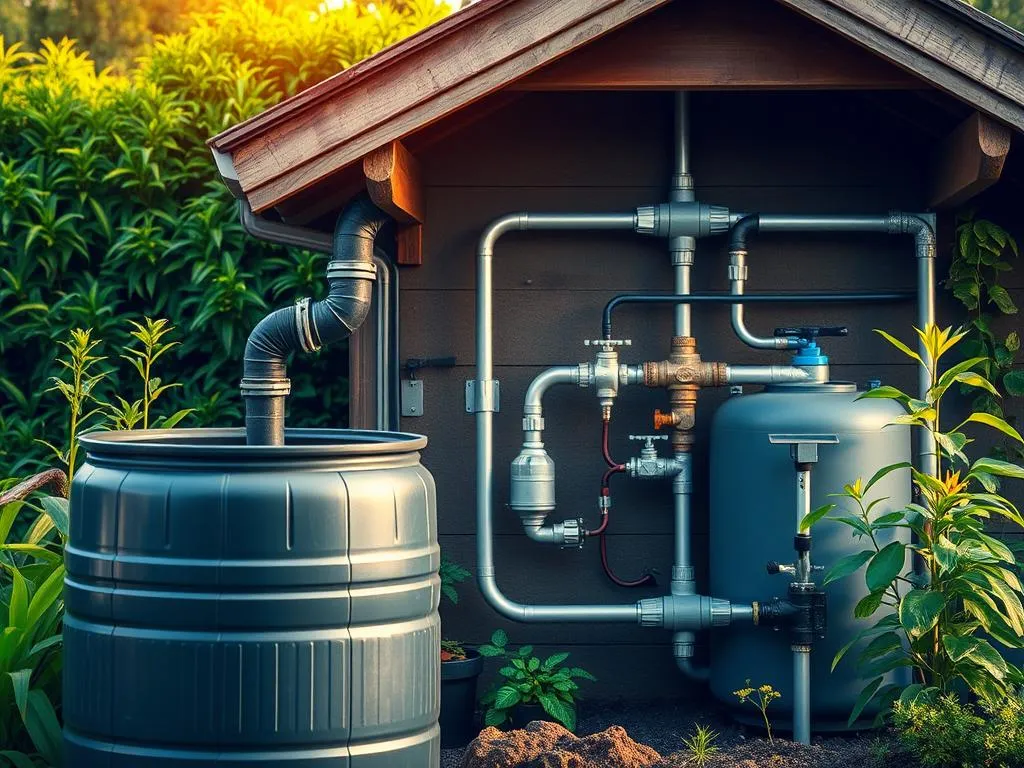
Rainwater harvesting is another excellent strategy for eco-friendly gardening techniques. By collecting rainwater in barrels, cisterns, or underground tanks, you can use it to water your garden instead of relying on municipal water supplies. This not only reduces your water footprint but also provides plants with naturally soft water that is free from chlorine and other additives. For example, directing rainwater from your roof into a collection system can supply your garden with a steady source of sustainable water during dry periods.
In addition to these methods, eco-friendly gardening techniques encourage xeriscaping—designing landscapes that require minimal water. This involves selecting drought-resistant plants such as succulents, native grasses, or ornamental grasses that thrive in local conditions. Xeriscaping also reduces the need for frequent mowing, which in turn lowers carbon emissions from gas-powered equipment. To implement this approach, assess your region’s climate and choose plants that are adapted to local rainfall patterns and soil types.
Natural Pest Control: Eco-Friendly Gardening Techniques to Reduce Chemical Use
Pests can be a constant challenge in any garden, but eco-friendly gardening techniques offer alternatives to chemical pesticides that protect both your plants and the environment. By using natural pest control methods, you can maintain a healthy ecosystem while avoiding the harmful effects of synthetic chemicals. Beneficial insects are a powerful ally in eco-friendly gardening techniques. Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory wasps, for instance, feed on aphids, mites, and other harmful pests, keeping their populations in check without the need for toxic sprays. To attract these insects, plant flowers like marigolds, daisies, and yarrow, which provide nectar and pollen. These plants also emit scents that repel pests, making them a dual-purpose addition to your garden. By fostering a habitat-friendly environment, you create a natural balance that supports biodiversity. Companion planting is another eco-friendly gardening technique that helps deter pests through plant interactions. For example, planting basil near tomatoes can repel aphids and improve the flavor of the tomatoes, while garlic and onions act as natural deterrents for insects like slugs and snails. This method not only reduces the need for chemical interventions but also enhances crop diversity and soil health. To maximize its effectiveness, research plant pairings that complement each other’s growth needs and pest resistance.

Homemade remedies like neem oil, vinegar solutions, or soap-based sprays are also part of eco-friendly gardening techniques. Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the neem tree, is a biodegradable pesticide that disrupts the life cycle of insects without harming beneficial species. Similarly, a mixture of water and vinegar can eliminate weeds and pests, while a solution of dish soap and water is effective against aphids and spider mites. These methods are cost-effective and eco-conscious, as they rely on natural ingredients rather than synthetic chemicals.
Composting: Eco-Friendly Gardening Techniques to Turn Waste into Wealth
Composting is one of the most impactful eco-friendly gardening techniques for reducing waste and enriching soil. By recycling organic materials into compost, you create a fertile growing medium that supports plant health and reduces the need for store-bought fertilizers. This process also diverts organic waste from landfills, where it would produce methane—a potent greenhouse gas.
To start composting, gather green and brown materials in equal parts. Green materials include vegetable scraps, grass clippings, and coffee grounds, while brown materials like dried leaves, branches, and paper provide carbon content. Layer these materials in a compost bin or pile, ensuring proper aeration and moisture levels to promote decomposition. Turning the compost regularly helps accelerate the process, while leaving it undisturbed allows for natural breakdown over time.
Eco-friendly gardening techniques also emphasize the importance of compost in soil health. When mixed into the soil, compost improves water retention, enhances nutrient availability, and encourages microbial activity that supports plant growth. For example, compost can help soil retain moisture during dry spells, reducing the frequency of watering. It also buffers soil pH, making it more resilient to changes in climate or soil conditions.
Moreover, composting can be integrated into your daily gardening routine. By composting food waste and garden trimmings, you reduce the amount of organic waste you generate and create a closed-loop system that benefits your garden and the environment. This practice not only saves money on gardening supplies but also reduces your carbon footprint by minimizing the energy required to transport and produce synthetic fertilizers.
Conclusion
Adopting eco-friendly gardening techniques is a practical and effective way to create a sustainable garden that benefits both your plants and the planet. From organic soil management to water conservation, natural pest control, and composting, these methods work together to reduce environmental impact while promoting long-term ecological balance. By prioritizing natural resources and low-impact practices, you contribute to global sustainability goals without compromising the beauty or productivity of your yard.
Whether you’re growing flowers, vegetables, or shrubs, integrating eco-friendly gardening techniques into your routine can lead to healthier plants, soil enrichment, and reduced resource consumption. Start small by experimenting with one or two practices, and gradually expand your approach as you become more familiar with eco-conscious methods. With consistent effort and mindful planning, you’ll create a garden that thrives in harmony with nature, making every plant and blade of grass a step toward a greener future.
In the end, eco-friendly gardening techniques are not just about growing plants—they’re about fostering environmental stewardship. By making conscious choices, you can minimize waste, preserve water, and support biodiversity in your own backyard. As more people recognize the importance of sustainable gardening, these practices become essential tools for creating a resilient ecosystem that sustains life for generations to come.